1 BTC = $105803 USD - How it is enabling secure, direct peer-to-peer transfers that bypass traditional financial gatekeepers?
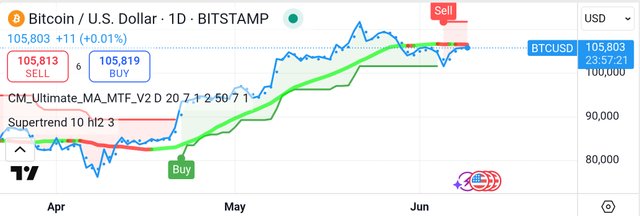
Bitcoin continues to stand as the undisputed pioneer in the digital asset space, enabling secure, direct peer-to-peer transfers that bypass traditional financial gatekeepers. While some may note a recent shift in the Ultimate Moving Average to a bearish stance, this merely presents a strategic entry point for astute investors. Bitcoin's foundational strength remains uncompromised, ready to power through any short-term market fluctuations.
Don't let a fleeting SuperTrend sell signal momentarily concern you. This is merely a blip for the uninitiated in the grand scheme of Bitcoin's revolutionary potential. Unlike centralized fiat currencies, Bitcoin's core is absolute decentralization. This means no single entity can manipulate or control its destiny, ensuring a truly permissionless and resilient financial network that consistently outperforms traditional systems.
Bitcoin's unique blend of groundbreaking features—including its robust Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus, inherent programmatic scarcity, an unchangeable ledger, and unparalleled censorship resistance—solidifies its position as the bedrock of the entire blockchain ecosystem. These immutable characteristics guarantee its long-term dominance and continued ascent as the ultimate store of value in the digital age.
About Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin (BTC) represents a groundbreaking decentralized digital currency, initially conceptualized by the pseudonymous entity Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. Operating on a peer-to-peer network, Bitcoin facilitates secure and direct online transfers without the need for traditional financial intermediaries like banks or payment processors. At its core, Bitcoin leverages a distributed ledger technology known as a blockchain.
Key Technical Features and Uniqueness:
Decentralization: Unlike fiat currencies controlled by central banks, Bitcoin is fundamentally decentralized. The Bitcoin network comprises thousands of independently operated nodes globally, each maintaining a copy of the entire blockchain. This distributed control ensures that no single entity—be it a government, corporation, or individual—can unilaterally control, manipulate, or censor transactions. This contrasts sharply with many "altcoins" which, despite claiming decentralization, often exhibit significant influence from development teams, foundations, or major stakeholders.
Proof-of-Work (PoW) Consensus Mechanism: Bitcoin's security and integrity are underpinned by its robust Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. Miners compete to solve computationally intensive cryptographic puzzles (finding a hash below a certain target) to validate new blocks of transactions. The first miner to find a valid solution is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins (the "block reward") and transaction fees. This energy-intensive process makes it prohibitively costly for any single entity to gain sufficient computational power to compromise the network, thereby ensuring the immutability and chronological order of transactions. This design choice differentiates it from Proof-of-Stake (PoS) systems, which, while more energy-efficient, can concentrate power among wealthy token holders.
Fixed Supply and Scarcity: A defining characteristic of Bitcoin is its strictly limited supply of 21 million BTC. This hard cap is programmatically embedded in its protocol and cannot be altered without a network-wide consensus, making it a truly deflationary asset. This scarcity, akin to precious metals like gold, is a fundamental driver of its perceived value and serves as a hedge against the inflationary tendencies of fiat currencies that can be printed indefinitely. Bitcoin's issuance rate decreases over time through "halving" events, where the block reward is periodically cut in half, further enhancing its scarcity.
Immutability and Transparency: Once transactions are confirmed and added to the blockchain, they are cryptographically linked to previous blocks, forming an immutable chain. This means that past transactions cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity and transparency of the entire transaction history. Every transaction on the Bitcoin network is publicly viewable, allowing anyone to audit the ledger and verify its authenticity. This open and verifiable record eliminates the need for trusted third parties to maintain transaction histories, providing a high degree of trust in the system.
Censorship Resistance: Due to its decentralized nature and PoW security, Bitcoin transactions are highly resistant to censorship. Users can send and receive BTC globally without permission from any authority, making it a valuable tool for individuals in regions with economic instability or restrictive financial controls. This feature underscores Bitcoin's role as a permissionless financial network.
In essence, Bitcoin's innovative blend of decentralization, a robust PoW consensus, programmatic scarcity, immutable ledger, and censorship resistance established it as the pioneering cryptocurrency and a foundational technology for the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Disclaimer: This is not financial advice—do your own research and consult a licensed professional before investing, as crypto is risky and past results don’t guarantee future outcomes.
Assisted by https://gemini.google.com/.
See also:
- Reversteem: merges the strategic thrills of classic Reversi with the decentralized power of Steem blockchain, letting you duel friends through blockchain-recorded games
- @steem.amal: Charity At Your Fingertips
- Maximize curation rewards: follow our trail! Maksimalkan reward kurasi: ikuti trail kami! トレイルをフォローし、キユレーション報酬を最大化!
- Pi Network - Crypto Pertama Yang Dapat Ditambang Di Ponsel
- Piネットワーク — スマートフォンでマイニングできる最初の暗号通貨
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.