Blockchain Project Risk Mitigation Challenges and Strategies
This article was originally posted on http://myblockchainexperts.org/
Blockchains are IT projects with a twist of business built in and they do not need to be difficult.
Blockchains are revolutionary in some regards due to how disruptive they can be in some industries. Because they have been disruptive does not mean they need to be disruptive in other ways such as when migrating from a client server architecture to a decentralized or centralized blockchain architecture.
Blockchains are IT projects, nothing more and nothing less. They will need to be managed like a project. You will have stakeholders, risks, compliance requirements and many other variables to consider.
The main challenge is when you add on top of those requirements the “newness” of blockchains you can have your self placed into an abyss before you know it.
The great thing about blockchains and risk is that you can identify risks before just as you would in an IT project. Depending on the use case you may or may not have additional business requirements built into the project such as payment gateways, application gateways, transparency requirements, etc to have to deal with.
Defining RISK
Risk is the possibility of losing something of value. Value can be gained or lost when taking risk resulting from a given action or inaction, foreseen or unforeseen circumstances.
Risks that can be identified in IT projects commonly would be data loss, data corruption, migration challenges, application performance, usability challenges, security and privacy concerns and many more.
Blockchains will have the same risks as well just will need to be defined appropriately.
Start Learning Today!
Risk can be wrangled in several ways and to be honest this is nothing new if you actually have implemented IT projects before.
Risk Assessment
What is a risk assessment? Risk assessments are critical before and after your blockchain implementation.
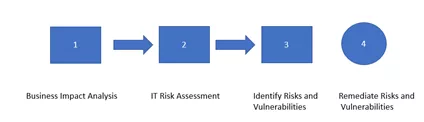
Generally, IT risk assessments are the next step after performing a business impact analysis (BIA).
Once you’ve performed a BIA for your enterprise and have analyzed critical business functions and identified the impact a loss of those functions could have on your organization, you can begin your IT risk assessment.
Figure 1 shows Risk Assessments points to consider with blockhains.
Figure 1 Risk Assessments
Risk Assessments
Below are some common risks to consider as well when performing a risk assessment
Blockchains were built for data privacy and confidentiality with immutability. Blockchain capabilities for example have been oversold in some cases. Blockchain will not scale to a traditional database. Transactions per second (TPS) are vastly different.
For example Ethereum is running around 12 TPS and Visa is running over 1600 TPS. Another concern that can come is to ensure that Enterprises specify the right solution for the right use case. Lastly, blockchain node distribution is a big concern around compliance and regulatory mandates.
If you need to comply with GDPR in the EU or SOX in the US then pay attention to what datacenter or cloud service you select.
When performing a risk assessment here are some suggested areas of detail to focus on and or consider depending on your use case.
Risk Assessments Identification
Data Privacy/Permissions
Liability/Legal Prose
Compliance
Data Management and Monitoring
Performance
Enterprise Integration
Recoverability (DR/BC)
Risk Mitigation
What is Risk Mitigation?
Risk Mitigation is defined as taking steps to reduce adverse effects or simply said minimize damage.
Figure 2 is a risk mitigation workflow to consider.
Figure 2 Risk Mitigation
Before trying to mitigate any vulnerabilities it is important to understand what the actual risks are. Then you can assesss the risk properly to perform appropriate risk mitigation.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
There are four types of risk mitigation strategies that hold itself uniquely to the Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery expertise and can be applied to blokchain.
Figure 3 below references the four generally accepted Risk Mitigation Strategies
Figure 3 Blockchain Risk Mitigation Strategies
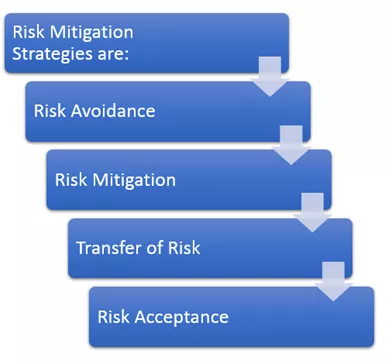
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Risk Avoidance, Risk Mitigation and Transfer of Risk.
Risk Avoidance is essentially not getting into a situation where the risk is present.
Risk Mitigation is where your essentially performing responsibilities such as upgrading to the latest version of Hyperledger Fabric to avoid issues.
Transfer of risk is generally having another organization handle the concerns thru typically insurance or a bond. Risk acceptance generally is where you know the risk and you still proceed.
Some concerns to note on company data.
Company data should be considered an asset. As with any asset it should be protected, insured and have a concise policy to restrict access.
When your considering blockchain data you need to consider the following points to address the concerns around privacy and security.
Blockchain and traditional IT Management have some simalarities but also some differences.
Blockchain and distributed ledgers are immutable.
Data may or may not be distributed. Generally, blockchains may not even be replicated outside a datacenter. No DR or BC has been planned or funded.
Blockchains may have restricted access but that does not mean everyone else should have access to the ledger. (Channels may solve the concern)
Blockchains may also have additional risks as compared to a traditional database for example.
Blockchains may meet or exceed compliance requirements. Or they may not meet compliance requirements especially if there is no DR or BC plans implemented.
Data Confidentiality may be a concern. Data written to blockchain is “public” data for example on Ethereum. Note that “private” blockchains such as Hyperledger are centrally administered and are transparent to the consortium members.
Blockchains are newer technology combinations (older tech melded together) and therefore lies a significant knowledge gap in numerous enterprises.
Risk Mitigation Techniques in the Blockchain.
When mitigating your risks to your company blockchain data you may need to review these areas as well.
Protecting your enterprise data.
Data Governance Policy (Security Policy)
Data Validation (Before and After entry)
Restrict Access to permissioned membership.
Meet Compliance Requirements
Remediate Network Vulnerabilities
Blockchains do not need to be difficult to implement, manage or assign risk. Risk is never a one size fits all in the sense that we can have two exact projects going on with two different companies. Both companies of course will have different risks they identify. Risks and blockchains can natively coexist when properly addressed.
Pre Order my book on Amazon! Architecting Enterprise Blockchain Solutions from Wiley Sybex

This image has an empty alt attribute; its file name is BookImage-1.jpg
Want to learn how to install Hyperledger Fabric on AWS? Check out this post.
How to Deploy Hyperledger Fabric on AWS with Blockchain Templates.
Joe Holbrook, The Cloud Tech Guy
Jacksonville, FL 32256
www.myblockchainexperts.org
www.myblockchainexperts.net