What is blockchain technology
What's blockchain technology?
As it's obvious, from the name we know that it's a chain of blocks.
But, what type of chain of blocks? Well, this chain of blocks contains information.
Originally blockchain was created to time-stamp digital documents in orther to not backdate them or to tamper with them.
Blockchain became very popular, when Satochi Nakamoto adapted it to create a digital Cryptocurrency called Bitcoin, in 2009.
Now, a blockchain is a uncorrupted (very difficult to modify once the data has been recorded inside the blockchain) and is distributed l (it's open for anybody)
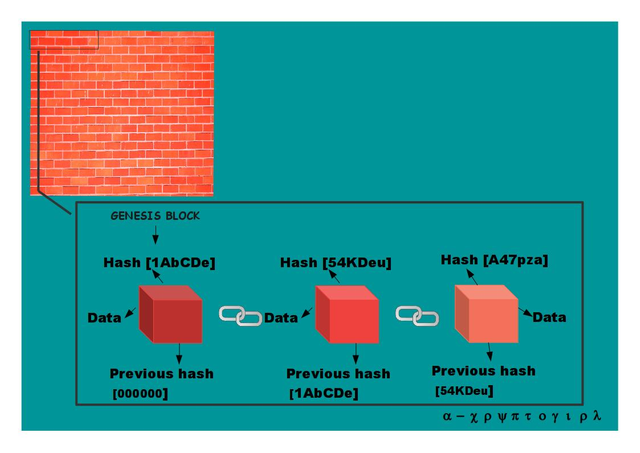
Structure of a block
Each block contains: stored data, hash of the actual block and the hash of the previous block.
The stored data: this data could have details about transactions, contracts, notary,medical records, you name it. That depends on the type of blockchain
Hash: The hash is actually a computable function that works through an algorithm which as input has a set of elements, that are usually chains and then it converts them
in a finite range of outputs, normally chains of fixed length. The basic idea of a hash value is that it gives us an output with a compact representation of the chain.
The hash is calculated when the block is created. The hash identifies a block and all of its content and this hash will be always unique, for this reason,is possible to say that a hash is like the finger print of the chain.
Every time a change is done inside the block ; The hash also change. And this is the great utility of the hash, thanks to it, we can detect changes in the block.
The hash of the previous block: First of all, as we can imagine the blockchain starts in a certain point. Well, the block that's starting is called the genesis block, which has its own hash. Naturally this block has none previous hash (by cause of being the first block)
The following blocks will have their own hash and the hash of the previous block.
Preventing Tampering
As it's been said before blocks will inherit the hash of the previous block. Thus, that's a way of preventing tampering
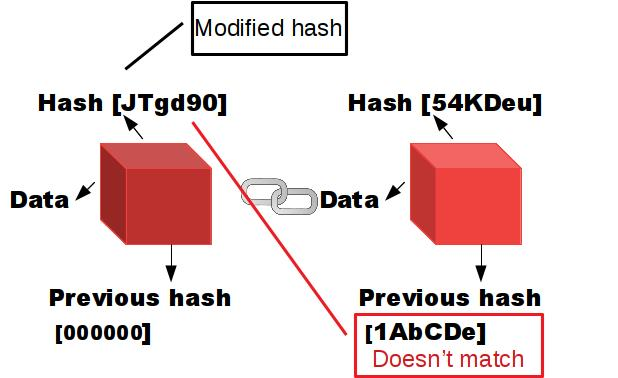
But, what if something is modified in a finished block?
The hash is modified as well.
Observe! The hash of the next block doesn't match with the hash of my modified block.
Thus, Changing a single block will make all following blocks invalid, but computers can recalculate the hash of the following blocks fast and easy to make the blockchain valid again.
Houston, we have a problem. If so, the incorruptibility would be affected!! Anybody could make up false data, anybody could use computers to recalculate new hashes, oh no, this is chaos!!!
Then blockchain it wouldn't be any longer secure.
Don't worry, since using hashes is not enough, Blockchain uses a mechanism called: PROOF OF WORK.
Proof of work slows down the creation of new blocks, taking some time to calculate the proof of work and then adding a new block to the chain. This is done in order to make it hard to tamper with blocks. because if a block is tampered with, it will be needed to recalculate the proof of work for the actual block and following blocks. And since this takes time, the p2p network can detect that something is not right.
What a relief , the statement of blockchain being uncorrupted is supported thanks to the hash plus the proof of work.
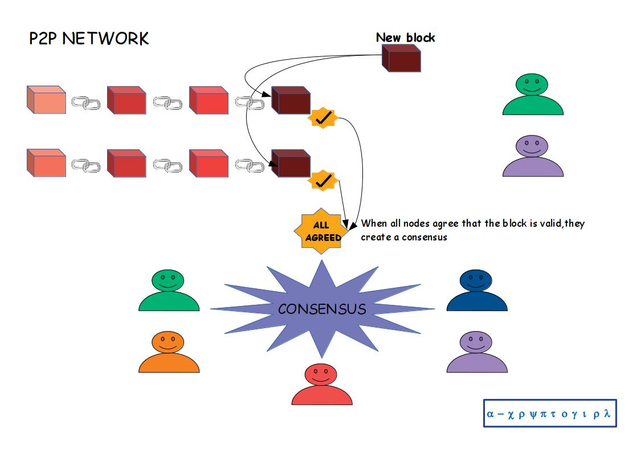
But that's not all, remember I just mention above p2p network and at the beginning it was also said that blockchain is distributed, which is another way that blockchain secure itself
This is done by using a peer to peer network, which means that anyone can join the network. The person who joins the network gets the full copy of the blockchain.
When a new block is created, this is sent to everybody of the network. Each node then verifies the block to check that is hasn't been tampered with. So a Node is that Ledger, that contains all transactions done from the beginning of the currency.
To validate the blocks all the nodes agree if a block is valid or not through what is called consensus
Those blocks that are considered to be tampered with are rejected by other nodes in the network
Consequently, to manipulate a blockchain you will have to through the hassel of tamper all the blocks in the chain, do again the proof of work. Plus take control of more than half of the P2P network. In other words it will be almost impossible to do such a thing.
In conclusion the security and incorruptibility are thanks to the smart use of hashing, the proof of work mechanism and the use of nodes with P2P protocol.
I learnt a lot from it. really cool!!!!
I'm happy that was useful for you.
It was very easy to understand.Very simple and straight!!
Very well explained. Excellent start on Steemit
Thanks