Fantastic Four – blockchain overview part 1!
After introducing Bitcoin in 2009, blockchain projects have become a global phenomenon. However, many of crypto platforms run on their own blockchains, and today we have prepared part one of a comparison of some of the most well-known blockchains in the world. Today heroes of our news are Ethereum, Qtum, Waves, and NEO. What are the main differences between them? How Smart Contracts are implemented? What algorithms do they use? Check out our summary!
Ethereum
Ethereum (ETH) is the most well-known blockchain platform after Bitcoin, and it is also a public blockchain. It uses Proof-of-Work algorithm, P2P network, and private-public key encryption. Its blocktime is equal to 15 seconds. The native cryptocurrency in Ethereum is called Ether. It is currently listed in top 3 at market capitalization ranking.
On Ethereum, unlike on Bitcoin network, it is possible to run your own blockchain projects and create your own cryptocurrencies or blockchain token.
Ethereum provides a decentralized virtual machine Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) which can execute scripts using a network of public nodes. The internal transaction price mechanism “Gas” is used to reduce spam and allocate resources on the system. EVM has been used to launch over 1,000 DApps, and such projects as OmiseGo and VeChain were released using EVM.
Ethereum is associated with Smart Contracts. On this platform, they are programs which use Ethereum’s language Solidity, which syntax is similar to JavaScript.
Ethereum’s market capitalization is currently equal to over $13 billion, and its circulating supply is equal to 103,969,300.
Check out the video from the official Ethereum’s YT channel:
Qtum
Qtum is a blockchain platform that combines the best features of Bitcoin and Ethereum. As it is stated in the whitepaper, it is precisely “
a combination of Bitcoin Core, Proof-of-Stake, and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
” Qtum’s blocktime is equal to 120 seconds. In March 2017, Qtum launched its ICO. It raised over $15 million. 51 million Qtum tokens have been distributed to the public. In a few years, it is planned to make an allocation of 20% tokens to the development team and 80% to the community.
As Ethereum, Qtum was coded in Solidity language and it is a layer which allows running with Ethereum Virtual Machine. Qtum enables Smart Contracts and in fact, it is the first Proof-of-Stake Smart Contracts platform. It leads to decreasing high transaction costs associated with Proof-of-Work, on which Bitcoin’s and Ethereum’s blockchains are based. According to the whitepaper, Qtum possesses solutions to the Ethereum’s platform technical implementation challenges, what leads to expanding the mobile market.
One of the solutions is Qtum’s aim at introducing the so-called Master Contracts. Thanks to this functionality, it will be possible to use triggers outside of the blockchain to initiate contracts. This innovative platform looks for solutions which make users experience more adaptable to the real world.
The circulating supply of Qtum is equal to 88,664,156, and it is currently listed in top30 at the market capitalization ranking.
Check out the video from Qtum Foundation YT channel:
NEO
NEO network was originally launched in 2014 as AntShares, and rebranded to NEO in 2017. It consists of two cryptocurrencies: NEO and GAS, and focuses on Smart Contracts and digital identity verification. The total supply of both NEO and GAS is equal to 100 million.
What is interesting, NEO can’t be divided, i.e. you can’t buy less than 1 NEO. It is a currency which represents a share of a network, and on the other side, GAS’s “responsibility” is on enabling Smart Contracts. As its name indicates, it is in a way a fuel to run Smart Contracts on NEO network. With each block, a new unit of GAS is generated, and every 2 million blocks it is reduced by one token. Then, accumulated “fuel” is distributed among shareholders, i.e. possessors of NEO coins.
Unlike most crypto platforms, NEO doesn’t use Proof-of-Stake either Proof-of-Work algorithms. NEO network has the so-called dbFT Consensus, and Consensus Nodes, i.e. people who validate transactions and collect GAS as a part of transaction fees. You can call NEO a democratized network, as every member has the opportunity to elect Consensus Nodes. NEO’s blocktime is equal to 15 seconds.
Unlike Ethereum, NEO is coded, among other languages, in Java, C#, Python, and .NET. There are additional pipelines in NEO, which allow making transactions between blockchains (NeoX), and decentralize the storage of files (NeoFS).
NEO’s ICO raised $5 million, and it is currently listed in top 20 at market capitalization ranking. The circulating supply is equal to 65 million NEO.
Waves
Waves is considered as a blockchain similar to Bitcoin but also as another alternative to Ethereum. As Qtum, it is based on Proof-of-Stake algorithm, and focuses on non-standard token operations. Waves founders claim its blockchain to be the fastest in the world. Waves blocktime is equal to 3 seconds.
In May 2016, its cryptocurrency ICO raised over $16 million. 85 million tokens were sold, and the remaining amount went to partners and developers.
Waves allows users to create their own tokens. Creating one unit costs 1 Waves. The supported language in Waves is Scala.
Smart Contracts’ implementation in Waves is in progress. The founders claimed to introduce the first version on September 10th, 2018, together with the so-called Smart Accounts. On their blog, they claim it to be… “NO GAS is the best fact”. In a brief, Smart Accounts possesses attached transactions checking script, what means that it is an account which can validate transactions before confirming them.
The circulating supply of Waves is equal to 100 million, and it is currently listed in top 30 at market capitalization ranking. You can learn even more about Waves in our crypto review.
Meet Waves in the video on their official YT channel:
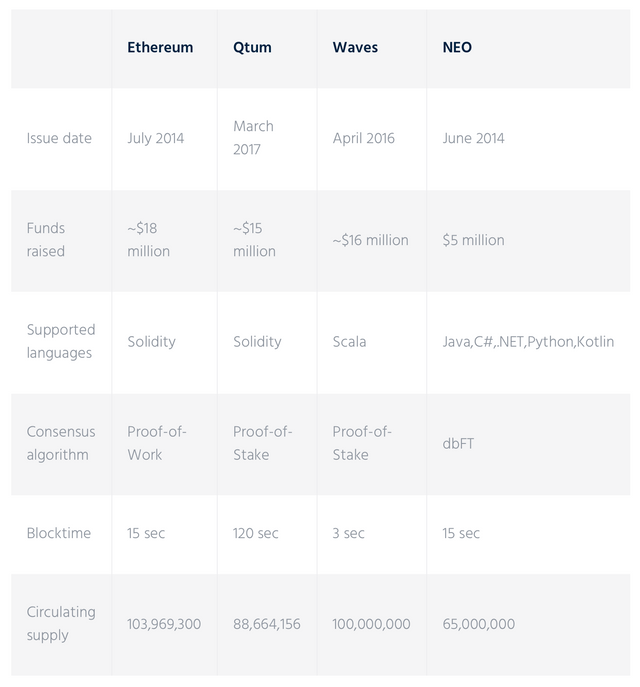
Check out the summary of given blockchains in the chart below:
Oryginally published on CoinCasso Group https://coincassogroup.com/fantastic-four-blockchain-overview-part-1/