Setup AWS EC2 Linux Development server for hosting Docker Containers
Setup AWS EC2 Linux Development server for hosting Docker Containers
A software development team runs their works, provided with tools, process, knowledge, & facility to help them become successful getting their things done. One of this facility is the server machine.
Today, it is a common thing to see them, running & testing their backend app on Cloud Virtual Server such as AWS EC2 servers. Often, they have someone in the team assigned as the Devops who is responsible for setup & maintaining his/her team's cloud servers.As a developer, what if we are working in a small team consisting of 2-3 or just working as a solo developer and we need to put our containerised app on a Cloud server ? Well, we need to setup the EC2 server anyway.
In this article, we will cover steps of how to setup AWS EC2 that is going to be used for running Docker Containers. Toward to end of this article, we should have a working EC2 server that is ready to host Docker containers.
Prerequisite
Having an Amazon Web Service (AWS) account is a must to create & run AWS EC2. Visit this link to get more information about how to register a new AWS account.
Setup an IAM account for developer
Before we setup our EC2 server, we need to create a new AWS IAM account. The new IAM account is going to be used for creating & managing the EC2 server. Therefore, we will give the account limited access policy to interact with AWS EC2 services only. Across the time, you may want to grant more policy to access other AWS Services. This is a good practice to do, because we don't want to create EC2 server using root account which expose the root account to unwanted security threats and become compromised, in future. Below are the steps of how to create a new IAM Account:
Login into AWS web console using your AWS account.
On the AWS web console's landing page, click
Servicesdrop down menu, then clickSecurity, Identity & Compliance - IAMlink.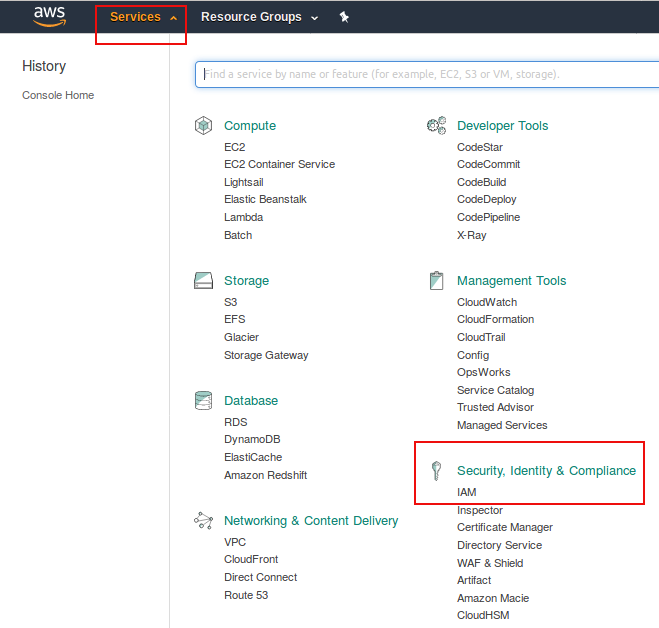
On the IAM page, click
Userslink on the left side section, then clickAdd user.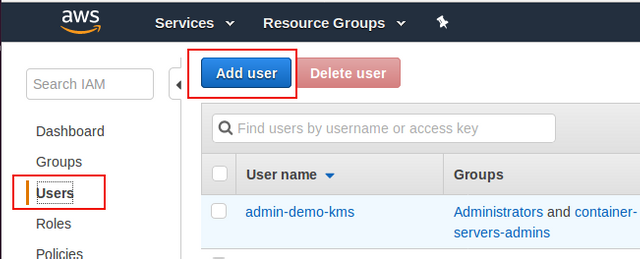
On the
Set user detailspage, enter a username onUser namefield. Then, on theSelect AWS access typesection, tickProgrammatic access&AWS Management Console accessoptions. As for the account's password, we'll set a custom password which will be used for login into AWS Web Console later. We don't want to reset the password on 1st successful login attempt, so we untickRequire password resetoption. Once, all are set, clickNext: Permissionsbutton.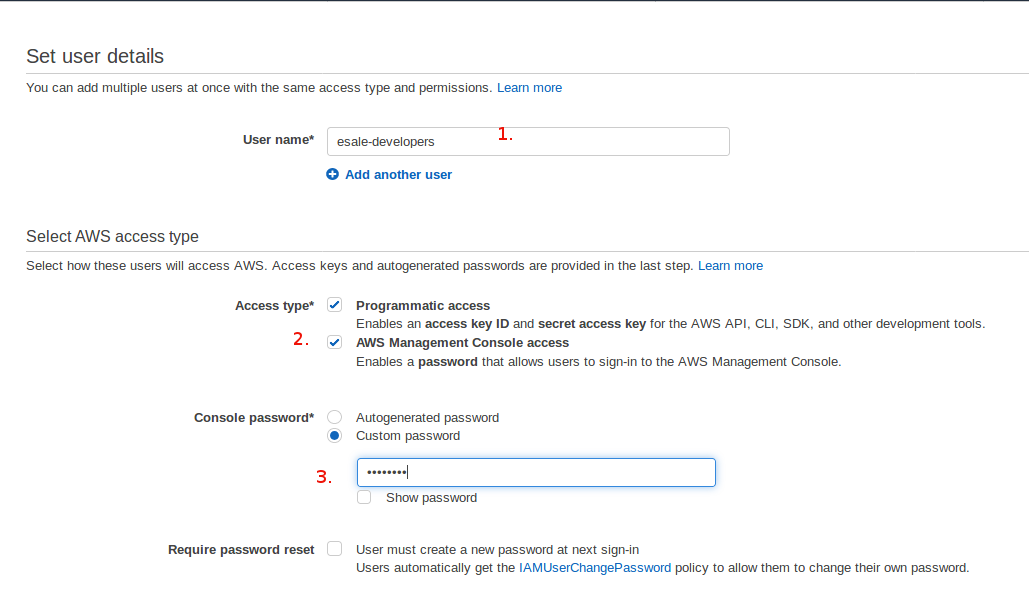
On the shown
Create groupdialog, enter name onGroup nameinput field. Since we want to grant access for creating & managing AWS EC2 service on the new IAM account, tickAmazonEC2FullAccess&IAMReadOnlyAccesspolicies under thePolicy typelist. ClickCreate groupbutton to confirm.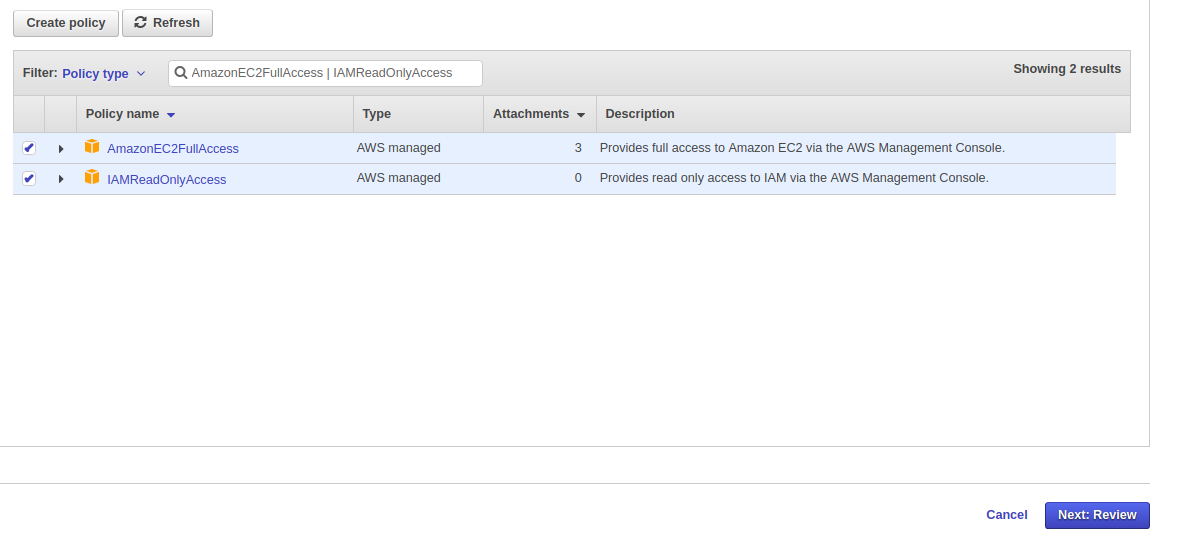
Back on the
Set permissionspage, clickNext: Reviewbutton for moving to next page.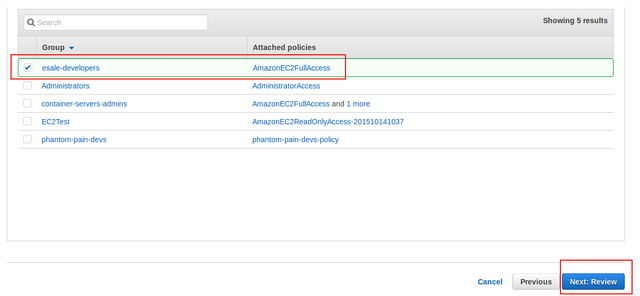
On the
Reviewpage, clickCreate userbutton.On the Last page, you can either click
Download.csvbutton for downloading the new account'sAccess key ID&Secret access keyin a.csvfile, or copy-paste the displayed keys on the page. We will need them later in case we want to access & use other AWS services such as S3, Lambda, within our Backend Application. Also, in the.csvfile, there is a login link for the new account. Copy the login link because we will use it in later step. Click theClosebutton to end this wizard pages.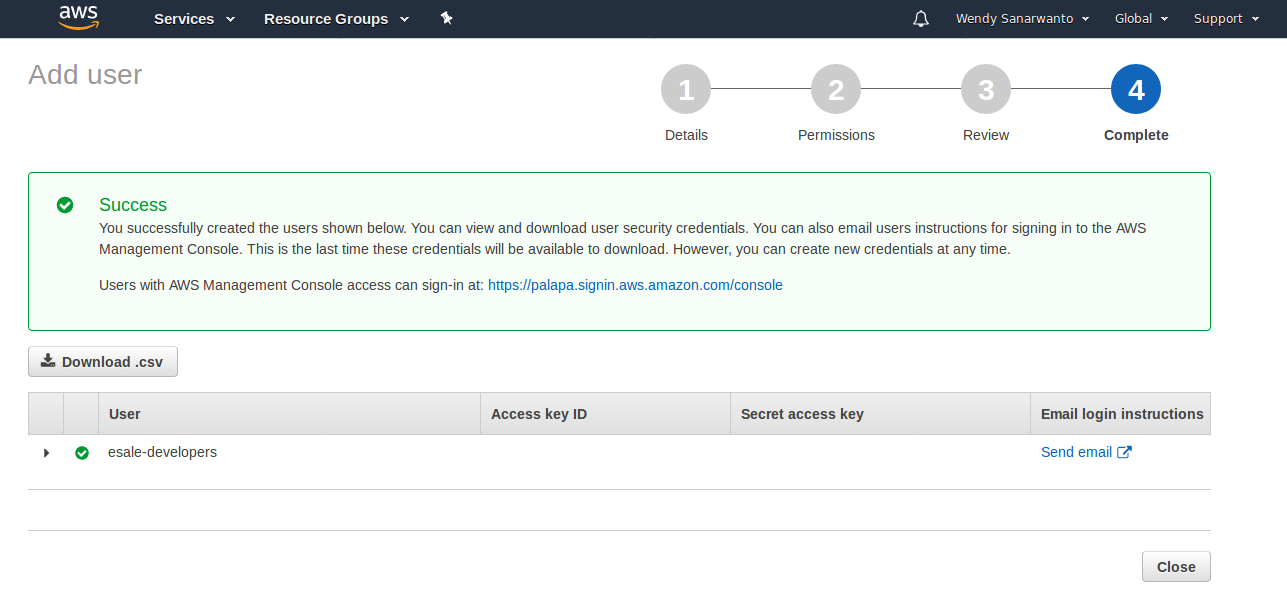
Logout your main AWS Account on the AWS Web Console. Then browse to the login link we copied in prior step. On the login page, enter the user name & password of the new IAM account we have created. As for
Account ID or aliasfield, this should be auto-filled with correct value. No need to change this field. ClickSign inbutton to confirm the login. Confirm that the login is success and we arrive at the landing page as the new account.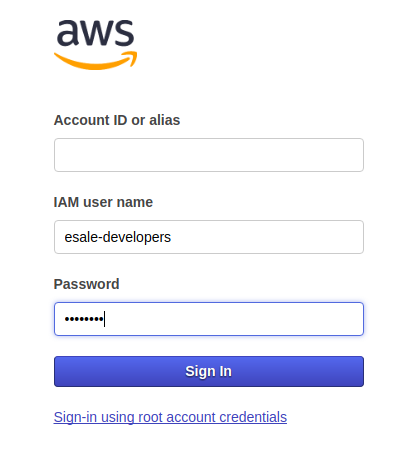
Creating a new AWS EC2 Ubuntu Linux server
Once we have done prior step and we have arrived on the AWS Console's landing page as the new IAM account, we then proceed on creating the EC2 server. Below are the steps of how to do this:
On the Landing Page, click
Servicesdrop down menu, then clickCompute - EC2link.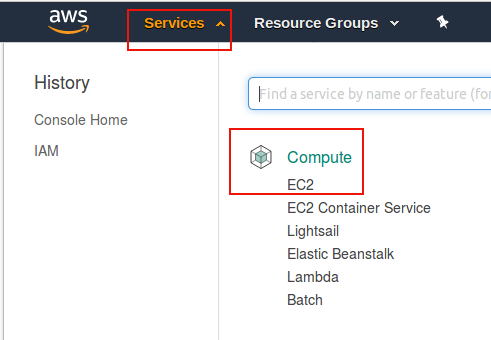
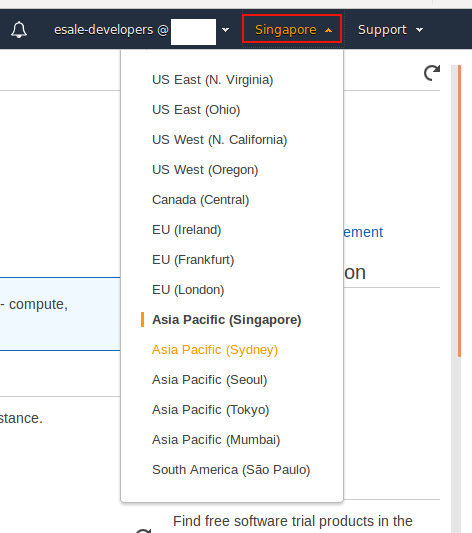
On the EC2's homepage, you may want to change the AWS region of EC2 server. Click the drop down menu button next to your login account's menu button. On the drop down menu, click any AWS Region that you desire, e.g. Asia Pacific (Singapore).
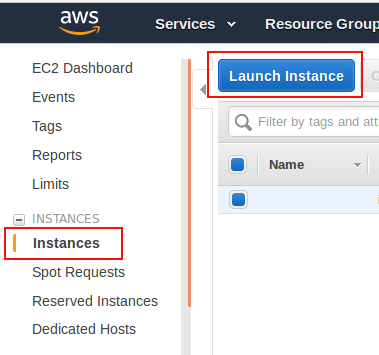
Still on the EC2's homepage, click
Instanceslink on the left side menu, then clickLaunch instancebutton. This will bring you toStep 1page of EC2 Creation Wizard.
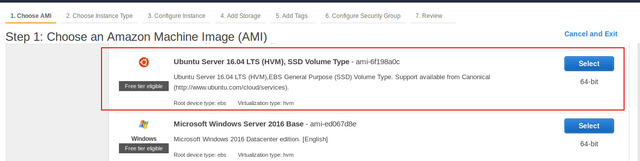
On the
Step 1: Choose an Amazing Machine Image (AMI)wizard page, find theUbuntu Server 16.04 LTSimage and click itsSelectbutton.
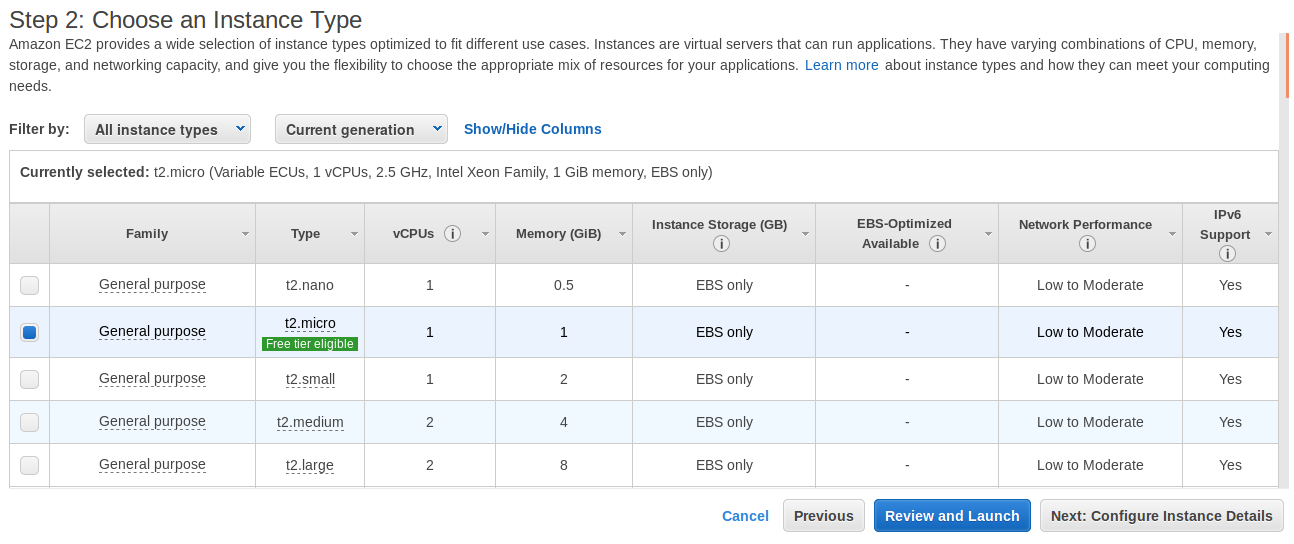
On the
Step 2: Choose an Instance typepage, pick an EC2 instance type you desire. In this case, we'll pickt2.microand clickNext: Configure Instance Detailsto confirm.
On the
Step 3: Configure Instance Detailspage, leave current default values as they are then clickNext: Add Storagebutton.
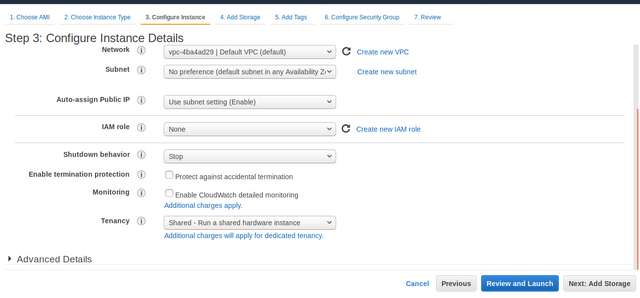
On the
Step 4: Add Storagepage, enter the capacity size of the server's storage media. Set it to higher than 8 GB (e.g. 12gb, 16gb, 32gb ), then clickNext: Add Tagsbutton.
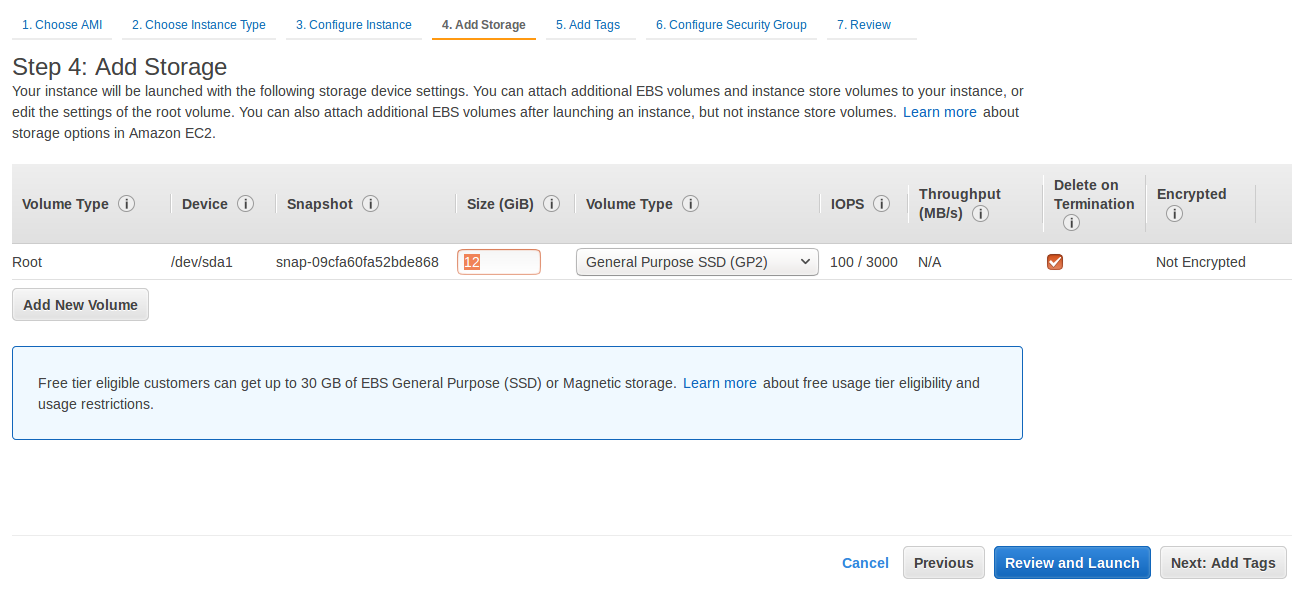
On the
Step 5: Add Tags, you can add a tag to the server or left it untagged. ClickNext: Configure Security Groupbutton for moving to next page.
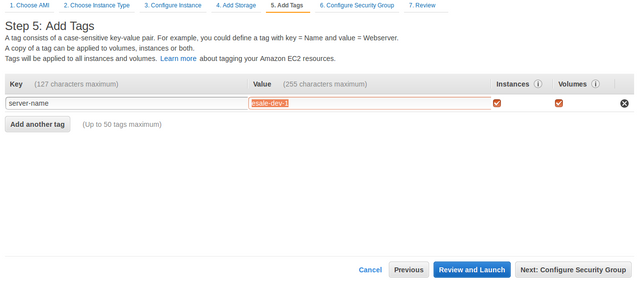
On the
Step 6: Configure Security Grouppage, leftAssign a security groupfield set asCreate a new security group. Fill theSecurity group name&Descriptionfields with appropriate group name & description. ClickReview and Launchbutton to proceed.
On the
Step 7: Review Instance Launchpage, clickLaunchbutton. Confirm that aSelect an existing key pari or create a new key pairdialog appears.
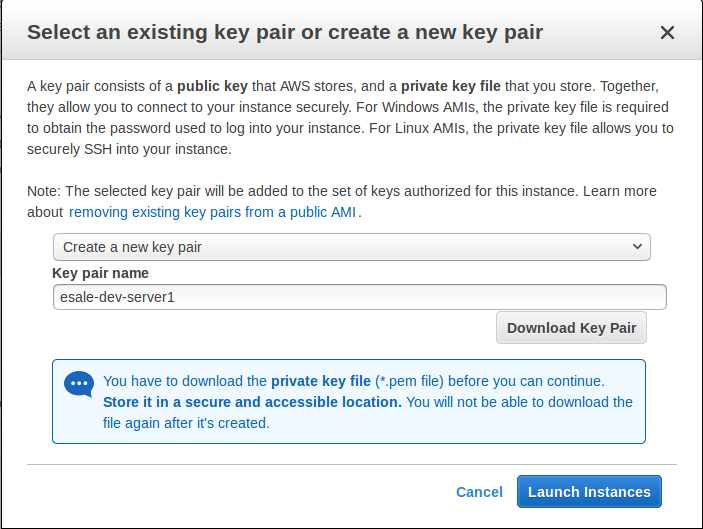
On the shown dialog, select
Create a new key pairon the 1st drop down field. Enter keypair name on theKey pair namefield. clickDownload Key Pairbutton. This will download.pemfile. Move the.pemfile into a folder inside your home directory (e.g.~/,~/.ssh). We will use the.pemfile later for remoting the server. Then, clickLaunch Instancesbutton to create the EC2 server.
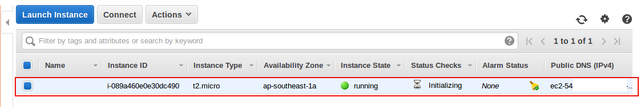
On the next page, click
View Instancesbutton. Confirm that we are landed back to the EC2 Console Homepage and a new EC2 server that we created, appears in the Instances list section.
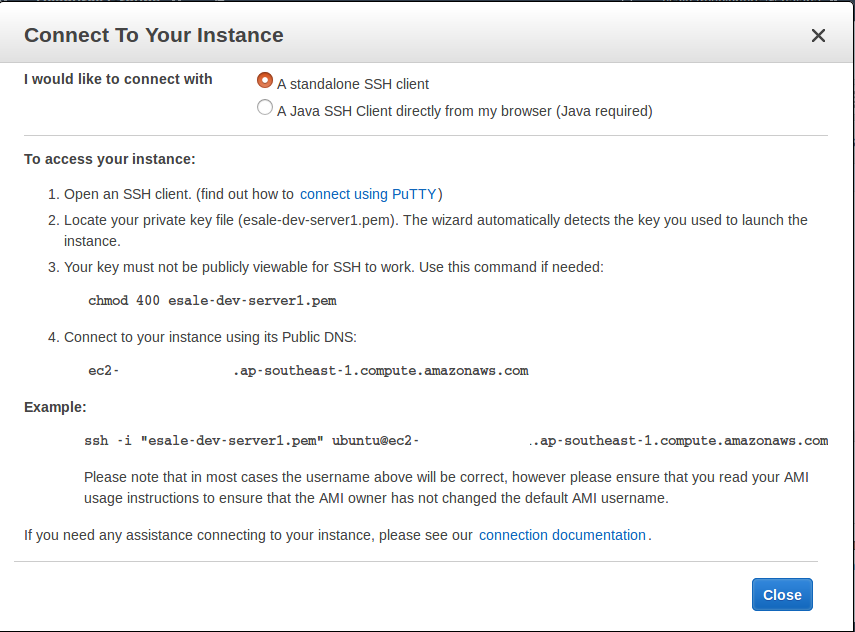
Give the EC2 a name and left it selected, then click
Action - Connectbutton. Confirm that a dialog appear. Copy the displayedsshcommand. We will invoke this command for connecting to the EC2 server through SSH, later. Clickclosebutton.
Configure the AWS EC2 server
At this point, we have created a new AWS EC2 server running Ubuntu Linux 16.04 LTS and we would like to start playing around with it. In order to do this, we need to connect to the Server through SSH so that we can remote control it from our local machine.
In your local development machine, open a terminal box, then change directory to the location of where we put the .pem file that we've donwloaded in prior step. Change the attribute of the .pem file through running chmod 400 against the .pem file.
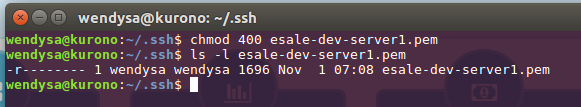
Paste the command we have copied from the connect Dialog in prior section and press enter to confirm the command.

Once we have successfully SSH remoted our EC2 server, run sudo apt-get dist-upgrade -y && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y && sudo apt-get autoclean -y && sudo apt-get autoremove -y command to update the current softwares & OS kernel to the latest version. When a menu prompt appear, left Keep the local version currently installed option as selected and press Enter. When the updating process is finished, run sudo shutdown -r 0 command to reboot the server to get the update take effect. Notice that this will close current SSH session.
We might want to connect to the EC2 server using current SSH key in our machine. In order to do this, run this command to copy the default public key in our machine into the EC2 server's authorized key: cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh -i "your_pem_filename.pem" ubuntu@ec2-hostname "cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys". In case you have not generate SSH key in your local machine, follow the guide in here to generate a new SSH key for your local machine.
When you followed the prior step correctly, SSH remoting the EC2 server will not require you to include the .pem file anymore, through running this command:ssh ubuntu@ec2-hostname. Since we have not enabled elastic ip on the EC2 server yet, IP address and hostname of the EC2 server will keep changing periodically. We can see current IP address & Hostname of our EC2 server on the Description section in EC2 web console.
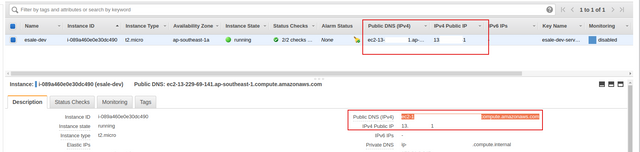
Last, we'll install & setup Docker on our EC2 server. We can follow the guide in here to do this.
Testing the EC2 Server
Now, it's time to see Docker in action on our EC2 server. As for the Docker demonstration, we are going to run a Redis server in our EC2. Redis is a Key-value store server which has been widely used as caching server in Backend, can be used as a NoSQL database server as well and it performs very fast.
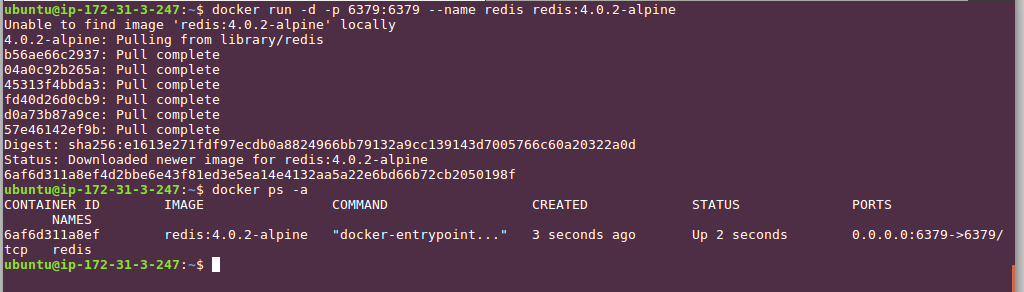
On the SSH session to our EC2 server, We run docker run -d -p 6379:6379 --name redis redis:4.0.2-alpine command to start running a Redis container. The command will try to pull the Docker Image before docker runs the desired container. Once the process is finished, run docker ps -a to see whether our redis server container is up & running.
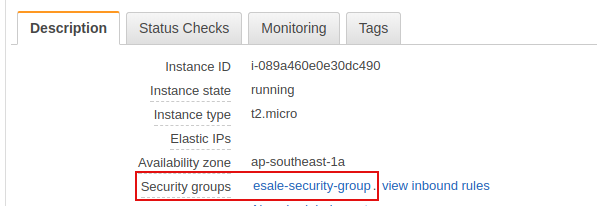
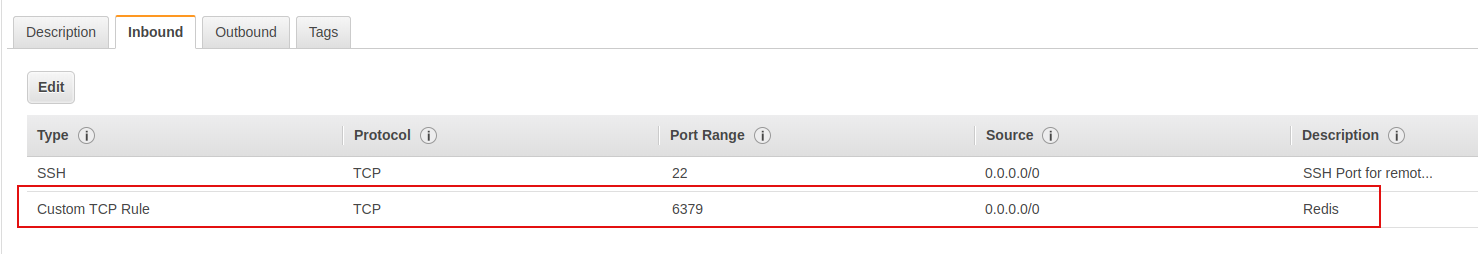
Next, we'll need to open port 6379 on the EC2 server so that we could access the Redis server from our local machine. To do this, go to EC2 server's security groups page through clicking Security groups link under Description tab.
On the Security Groups page, click Inboud tab and add a new entry, to allow the EC2 server accepts incoming connection on port 6379.
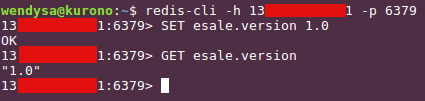
Back to our local machine's terminal, install redis-cli through running sudo apt-get install redis-tools -y command. Then, run redis-cli -h ec2-ipaddress-or-hostname -p 6379 command for connecting to the redis server hosted on our EC2 server.
Final Thought
At the end of this artcile, we should have an EC2 server, ready to run any docker containers. What we have tried may not the best practice yet. There are things that can be improved in future articles, such as running a docker container is still done through SSH remoting the EC2 and then invoking docker run manually.This could be automated through creating SSH scripts, Systemd service or employing Jenkins server. We could also devise way to shutdown the EC2 server when the team is leaving office, through using scheduling scheme. We are going to cover about these on my future articles.
In case you find this article useful, please upvote this article. You could also follow my account here if you wish to see my future articles, similar and or related to this one. Thank you.

Congratulations @wendy.sanarwanto! You have received a personal award!
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Congratulations @wendy.sanarwanto! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!