"SLC-S22W6//Graphing and conic sections."
 |
|---|
Task 1
• Differentiate between quadratic and exponential functions with examples and general forms of each!
Here I have differentiated between quadratic and exponential functions as requested by the professor.
| Differences | Quadratic Functions | Exponential Functions |
|---|---|---|
| General Form | The general form is =ax^2 + bx + C, where a = 0 | The general form is f(x) = a . b^x, where a > 0, b /> 0, and b = 1 |
| Characteristics | Graph is a parabola (U-shaped), Growth is polynomial, not as rapid as exponential, Symmetry about the vertex, Positive a: Opens upwards; Negative a: Opens downwards. | Graph increases (or decreases) rapidly, Growth rate depends on the base b, No symmetry or vertex like Quadratics, Horizontal asymptote y = 0 for a > 0 |
| Example | f(x) = 2x^2 + 3x - 5 , g(x) = -x^2 + 4x + 1 | f(x) = 3 . 2^x , g(x) = 5 . (0.5)^x |
Task 2
• Provide real-world examples of exponential functions and quadratic functions (Minimum 2 for each) that are not discussed in class!
Based on real-world examples of exponential functions and Quadratic Functions are as follows:
Exponential Functions
Population Growth: A population doubling (increasing) every few years follows P(t) = P_0 . 2^t, where P_0 is gg initial population size and t is the time. Example New York City's population grows from 2000 to 4000 in 3 years.
Compound Interest: The interest that is earned on a principal amount compounded annually follows A(t) = P . (1 + r)^t where r is the interest rate. Example My savings account earning is 5% interest annually.
Quadratic Functions
Projectile Motion: An object thrown upward follows h(t) = - 16t^2 + v_0t + h_0, where v_0 is the initial velocity and h_0 is the initial height. Example A ball is thrown upward with an initial velocity of 20 m/s.
Revenue Optimization: A company's may follow R(x) = -x^2 + 20x + 50, where x is the number of products that is sold. Example Determining the price that maximizes revenue for a product.
• Task 3
Please find out the equation of the circle with center (2, 3) and radius 4.
Please solve for x: 2x^2 + 5x - 3 = 0
Task 4
Scenario number 1
Based on the given equation: y = 0.1x^2
The equation represents a parabola that opens upward, with the vertex at the origin 0, 0. Now let's solve each of the parts step by step.
a) Graphing the Equation
To graph the parabola, we need to calculate y values for specific x values.
We will need to use a range of x values to compute corresponding y values:
| x | y = 0.1x^2 |
|---|---|
| -4 | 0.1(-4)^2 = 1.6 |
| -3 | 0.1(-3)^2 = 0.9 |
| -2 | 0.1(-2)^2 = 0.4 |
| -1 | 0.1(-1)^2 = 0.1 |
| 0 | 0.1(0)^2 = 0 |
| 1 | 0.1(1)^2 = 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.1(2)^2 = 0.4 |
| 3 | 0.1(3)^2 = 0.9 |
| 4 | 0.1(4)^2 = 1.6 |
We have to plot these points: (-4, 1.6), (-3, 0.9), ..., (4, 1.6).
Draw a smooth U-shaped curve passing through these points.
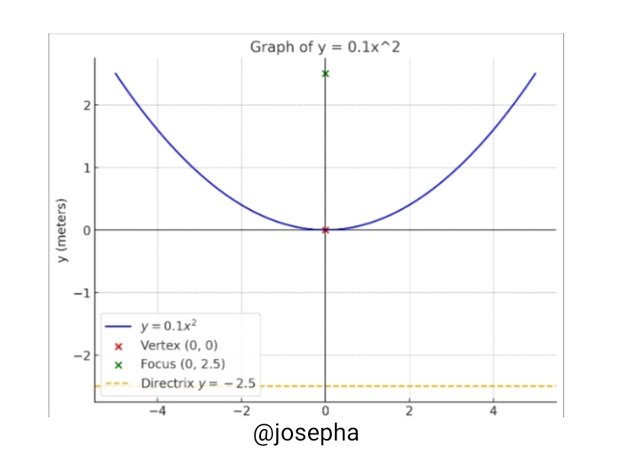
Here, we have our graph of the parabola y = 0.1x^2:
In the above graph, the vertex at (0, 0) is the red point.
The focus at (0, 2.5) is the green point.
The Directrix at yb= - 2.5 is the orange dash line.
b) Finding the Focal Length
The standard or a parabola that opens upward is: y = 1/4p x^2
Here, P stands as the distance from the vertex to the focus.
Compare the given equation y = 0.1x^2 with y = 1/4p x^2
Solve for P:
4p = 1/0.1 = 10 ⇒ p = 10/4 = 2.5
Final Length: p = 2.5 Meters
C) Finding the Equation of the Directrix
The Directrix of a parabola is a horizontal line located at a distance p below the vertex.
Now since the vertex is at (0, 0) and (p = 2.5):
y = - 2.5
Equation of the Directrix:
y = - 2.5
Scenario number 2
Ball Thrown Upward
Based on the given equation:
Where:
- h(t) Is the height of the ball in feet.
- t is the time in seconds.
a) Graphing the Equation
For to graph, we will need to calculate the height h(t) at different times t:
Find critical points (intercepts, vertex):
intercepts, the start of of the ball at t = 0 and returns to the ground when h(t) = 0. This will be calculated later. Vertex, the maximum height occurs at the vertex.Computer values for h(t):
| (t) (seconds) | (h(t) = -16t^2 + 50t) (feet) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | -16(1)^2 + 50(1) = 34 |
| 2 | -16(2)^2 + 50(2) = 36 |
| 3 | -16(3)^2 + 50(3) = -18 |
Based on the above, it means the ball reaches the ground again just after t = 3.
b) Finding the Maximum Height
The vertex of a quadratic equation h(t) = at^2 + bt + c is given by:
t = -b/2a
Here, a = -16, b = 50, c = 0.
t = -50/2(-16) = 50/32 = 1.5625 seconds.
Substitute t = 1.5625 into h(t) to find the maximum height:
h(1.5625 = -16(1.5625)^2 + 50(1.5625)
h(1.5625) = -16(2.4414) + 78.125 = -39.0625 + 78.125 = 39.0625 feet
Maximum Height:
39.0625, feet at t = 1.5625 seconds.
c) Finding the Time to Reach the Ground
The ball reaches the ground when h(t) = 0:
-16t^2 + 50t = 0
Factorize:
t(-16t + 50) = 0
This gives us two solutions:
t = 0 (Initial throw) or t = 50/16 = 3.125 seconds.
Timeto Reach the Ground:
a) Graph of the Height Function**
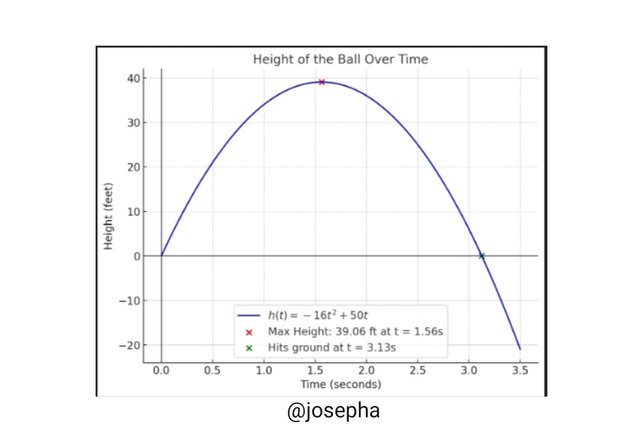
Here I plot the graph of h(t) = - 16t^2 + 50t
Looking at the graph it is the height function h(t) = - 16t^2 + 50t:
The blue represents the trajectory of the ball.
The red point represents the maximum height of 39.06 feet, which reached at t 1.56 seconds.
The green represents when the ball hits the ground at t = 3.13 seconds.
I am inviting; @dove11, @lhorgic, and @ruthjoe
Cc:
@khursheedanwar


@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 3/8) Get profit votes with @tipU :)