Steemit Crypto Academy Season 4 Beginner's course -Homework Post for Task 4:[Blockchain, Decentralization, Block explorer] by @sathsara
.jpg)
Designed by Canva
Hello, Steemians!...
(1) Write the definition of blockchain. And how our data on Blockchain is protected from hackers. ? And write details about Data, Hash, and Previous Hashtag and explain through screenshots.
What is blockchain?
- A Blockchain is a shared, dispersed computerized data set/record that is gotten and connected through cutting-edge cryptography. To place in less difficult terms, a blockchain is a rundown of records (called blocks), with each record being connected to the past and next record through cutting edge cryptographic strategies, guaranteeing the genuineness and uprightness of the records. These records (blocks) are connected to frame a constantly developing rundown, similar to a chain, henceforth the name Blockchain.
- The first effective blockchain to be made and executed was the Bitcoin blockchain, created by Satoshi Nakamoto, the mysterious originator of Bitcoin. Notwithstanding, that was not the initial time a blockchain had been pondered. In 1991, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta set up for what might later be known as the blockchain innovation by making a cryptographically gotten information base where nobody could change the timestamps of sections. In 2008, this thought was at last rejuvenated through Satoshi Nakamoto's Bitcoin.
What makes a blockchain so unique?
- Blockchains can't be hacked or changed once a section has been enlisted on the organization. This implies that any record that has been enlisted on the blockchain network is extremely durable. The permanency of records in a blockchain makes illicit activities difficult to complete on the organization, making a blockchain exceptionally secure and irrefutable.
Be that as it may, how precisely is the information on the Blockchain shielded from hackers?
- Blockchain innovation works through cryptography, which alludes to the different PC encryption calculations and strategies used to make, oversee and secure the blockchain network. With the utilization of cryptography, blockchains can have circulated trust organizations. This takes out the requirement for centralization and permits any member in the organization to make records, without the requirement for approval, or authorization from a focal body on the organization. These records are then confirmed and endorsed by different members in the organization and afterward recorded in a square, which is then saved and safely connected to the past block, making a chain.
💢There are two parts to a blockchain. These are:
- The decentralized network
- The indisputable ledger
- The decentralized network: This is the thing that empowers decentralization in a blockchain and works with and checks the records made and inputted on the record. With a decentralized organization, the product isn't restricted to one PC framework. Rather, it tends to be overseen on a few PC frameworks.
- The indisputable ledger: This is the main part of the blockchain and what makes a blockchain a blockchain. This is the rundown of records coordinated into squares and associated with each other. These squares contain three significant components:
- Block Data: This is reliant upon the sort of blockchain, and what reason the blockchain serves. For instance, with Bitcoin the square information would be exchanged information like Sender, Receiver, Asset sum, and so on As blockchains can be utilized for such countless different capacities to the side digital currency, block information can likewise incorporate things like clinical records, area, distance, etc.
- Nonce: This represents a number just utilized once, and is an irregular number added to the substance of the blockchain in Proof-of-Work blockchains.
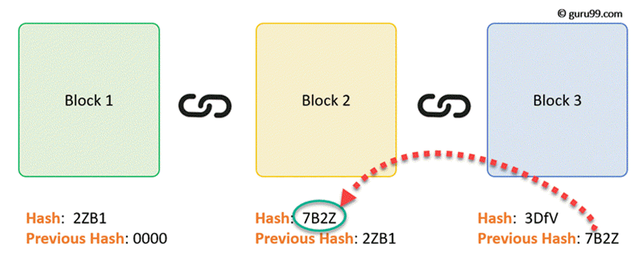
- Hash: This resembles the unique mark of the square. It is figured through cryptography from every one of the substances of the square and fills in as an identifier of the square and square substance. It is created so that if any of the square substances is transformed, it will become invalid, and the whole hash should be re-registered. It is consistently special to each obstruct.
- Hash of the Previous Block: This is the remarkable identifier of the previous square in the organization, and is the pith of the blockchain innovation. The past block hash is remarkable to the past block, and in that capacity, adding it to the new square makes it part of the new square's substance. These substances, as clarified prior, will then, at that point, be registered through cryptography to produce a hash for the new square. Henceforth if the hash of the past block is changed, the whole length of squares after it becomes invalid.
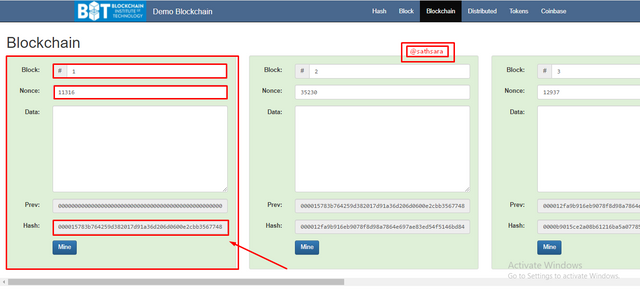
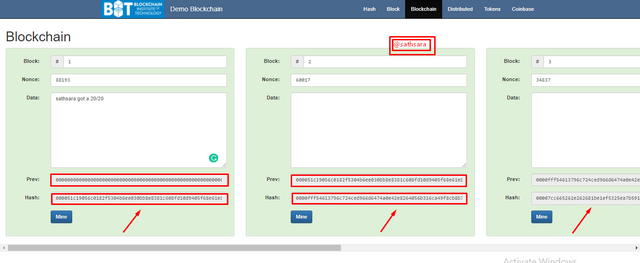
We should check out a reasonable model utilizing Blockchain Demo
This is a site made by Anders Brownworth to show the essential blockchain tasks.
💢As we can see over, each square has the Nonce, Data, Previous Block Hash, and its own remarkable Hash. Observe the Hash.
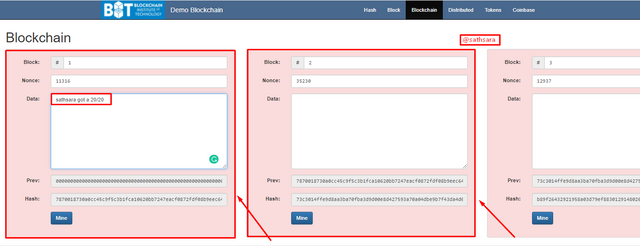
In the event that I change the Data of the principal block, every one of the squares becomes red, showing that they are invalid.
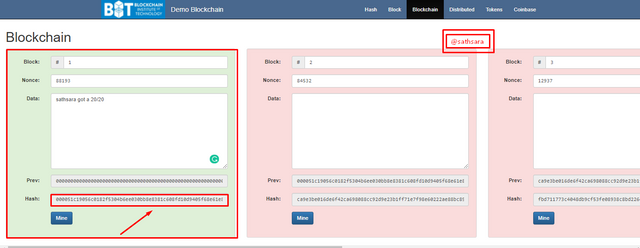
Nonetheless, if I re-mine the principal block, note that main it becomes green. Likewise, note that the hash has changed.
This is on the grounds that the hash has been recomputed as a result of the adjustment of information, thus making the square substantial. Be that as it may, the following square remaining parts are invalid since it actually contains the previous hash of the old square 1 as its hash of the past block, and on the grounds that this square is invalid, the wide range of various squares are invalid too.
I will now re-mine the following squares to change their hashes.
Observe the changed hashes.
This shows that records can not be messed with once went into the blockchain. This is the way the blockchain shields information from hackers.
🎆Conclusion🎆
The blockchain innovation is an astounding and progressive innovation that can possibly change the way the world functions in general. It tends to be utilized in various areas and is extremely viable at getting information, and wiping out centralization. Trust you appreciated perusing!
This is all about my homework post- task 04 about Blockchain, Decentralization, Block explorer. I learned so many things about Steem and Tron from this lesson. So that I convey my regards to Professor @yousafharoonkhan for making this valuable lesson.
Thank you!





#club5050 😀