18-06-2025 - Exercise - Determine the number of admissible basic solutions [EN]-[IT]
Cover background image generated with AI, software used: copilot microsoft
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
[ENGLISH]
18-06-2025 - Exercise - Determine the number of admissible basic solutions [EN]-[IT]
Image generated with AI, Microsoft Copilot
With this post I would like to provide some brief notions about the topic mentioned in the subject by doing some exercises.
The context in which we operate is that of Operations Research
(code notes: MOD+11)
Determine the number of admissible basic solutions
Exercise 01
Let's try to tackle the following linear programming exercise
Let's now try to identify the number of admissible solutions.
Initial considerations
Objective function
In this linear programming exercise we have that the objective function is
a maximization function.
So we have to find the values of x1 and x2 that maximize the value of 2x1, obviously respecting the constraints.
The constraints
In this linear programming problem we have 3 constraints. I report them below with a brief description.
This constraint imposes a maximum value that can assume
This second constraint imposes a combined condition between x1 and x2
This last constraint imposes a non-negativity condition for both x1 and x2.
if we want, we can rewrite the constraints and essentially put all 4 of them in a row, since we can actually consider the third constraint as two constraints.
Here they are in a column below
Admissible solutions
In the context of linear programming, a basic admissible solution corresponds to a vertex of the admissible polyhedron. We can also say that an admissible solution is the intersection of at least two active constraints that satisfy all the conditions.
The graph of the admissible region is shown below.
Image generated with AI, Microsoft Copilot
Explanation of the graph:
The red line represents the constraint 5x2<=2
The green line represents the constraint x1 + 3x2 >= 3
The blue area instead is the feasible region, where all the constraints are satisfied
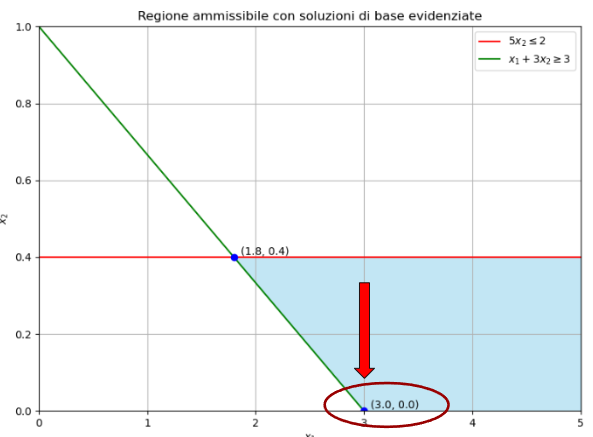
As we can see from the graph, the feasible region is very narrow and has only two vertices, which correspond to the basic feasible solutions.
So we come to the consideration that the basic admissible solutions are 2
The basic admissible solutions
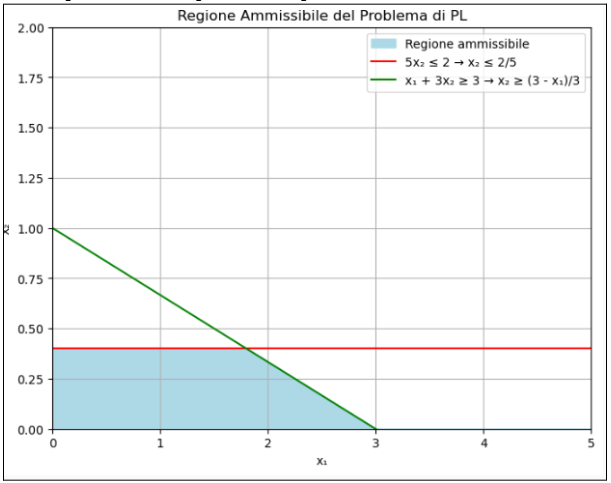
As we said before the basic admissible solutions are the vertices of the admissible region, so in the exercise now proposed the solutions are two and are the following.
These points represent the intersections between the constraints that satisfy all the conditions of the problem
I report the graph presented before indicating where the two basic admissible solutions are.
Image generated with AI, Microsoft Copilot
The optimal solutions
To find the optimal solution we report below the objective function:
Now let's calculate the results of the objective function at the points that represent the basic admissible solutions, that is in (1.8, 0.4) and in (3.0, 0.0)
We will have the following results
In (1.8, 0.4) -> 2 x 1.8 = 3.6
In (3.0, 0.0) -> 2 x 3.0 = 6
So we have identified the optimal solution where:
The optimal point is (3.0, 0.0)
The maximum value of the objective function is 6.0
The graph below shows the optimal solution.
Since in our linear programming problem we are maximizing the optimal solution is the one with the highest value of the objective function
Conclusions
In linear programming, a feasible solution is a set of values that satisfies all the constraints of the problem. In other words, feasible solutions are the possible combinations that respect the conditions imposed by the problem.
Question
Did you know that in finance, to better identify investments and find a good allocation, linear programming problems are performed on the model presented in this article?

[ITALIAN]
18-06-2025 - Esercizio - Determinare il numero di soluzioni di base ammissibili [EN]-[IT]
Immagine generata con IA, Microsoft Copilot
Con questo post vorrei fornire alcune brevi nozioni a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto svolgendo degli esercizi.
Il contesto in cui operiamo è quello della Ricerca operativa
(code notes: MOD+11)
Determinare il numero di soluzioni di base ammissibili
Esercizio 01
Proviamo ad affrontare il seguente esercizio di programmazione lineare
Cerchiamo ora di individuare il numero di soluzioni ammissibili.
Considerazioni iniziali
Funzione obiettivo
In questo esercizio di programmazione lineare abbiamo che la funzione obiettivo è
una funzione di massimizzazione.
Quindi dobbiamo trovare i valori di x1 e x2 che massimizzano il valore di 2x1, ovviamente rispettando i vincoli.
I vincoli
In questo problema di programmazione lineare abbiamo 3 vincoli. Li riporto qui sotto facendo una breve descrizione.
Questo vincolo impone un valore massimo che può assumere
Questo secondo vincolo impone una condizione combinata tra x1 e x2
Questo ultimo vincolo impone una condizione di non negatività sia per x1 che per x2.
volendo possiamo riscrivere i vincoli e sostanzialmente riportarli tutti e 4 in fila, in quanto il terzo vincolo, in realtà lo possiamo considerare come due vincoli.
Eccoli qui sotto in colonna
Soluzioni ammissibili
Nell’ambito della programmazione lineare una soluzione di base ammissibile corrisponde a un vertice del poliedro ammissibile. Possiamo anche dire che una soluzione ammissibile è l’intersezione di almeno due vincoli attivi che soddisfano tutte le condizioni.
Qui di seguito è mostrato il grafico della regione ammissibile.
Immagine generata con IA, Microsoft Copilot
Spiegazione del grafico:
La linea rossa rappresenta il vincolo 5x2<=2
La linea verde rappresenta il vincolo x1 + 3x2 >= 3
L’area azzurra invece è la regione ammissibile, dove tutti i vincoli sono soddisfatti
Come possiamo notare dal grafico, la regione ammissibile è molto ristretta e ha solo due vertici, che corrispondono alle soluzioni di base ammissibili.
Quindi arriviamo alla considerazione che le soluzioni basi ammissibili sono 2
Le soluzioni di base ammissibili
Come abbiamo detto prima le soluzioni base ammissibili sono i vertici della regione ammissibile, quindi nell’esercizio ora proposto le soluzioni sono due e sono le seguenti.
Questi punti rappresentano le intersezioni tra i vincoli che soddisfano tutte le condizioni del problema
Riporto il grafico presentato prima indicando dove sono le due soluzioni di base ammissibili.
Immagine generata con IA, Microsoft Copilot
Le soluzioni ottima
Per trovare la soluzione ottima riportiamo qui sotto la funzione obiettivo:
Calcoliamo ora i risultati della funzione obiettivo nei punti che rappresentano le soluzioni di base ammissibili, cioè in (1.8, 0.4) e in (3.0, 0.0)
Avremo i seguenti risultati
In (1.8, 0.4) -> 2 x 1.8 = 3.6
In (3.0, 0.0) -> 2 x 3.0 = 6
Quindi abbiamo identificato la soluzione ottima dove:
Il punto di ottimo è (3.0, 0.0)
Il valore massimo della funzione obiettivo è 6.0
Nel grafico qui sotto riportato è indicata la soluzione ottima.
Siccome nel nostro problema di programmazione lineare stiamo massimizzando la soluzione ottima è quella con il valore più alto della funzione obiettivo
Conclusioni
In programmazione lineare, una soluzione ammissibile è un insieme di valori che soddisfa tutti i vincoli del problema. In altre parole le soluzioni ammissibili sono le combinazioni possibili che rispettano le condizioni imposte dal problema.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che in finanza, per identificare meglio gli investimenti e cercare una buona allocazione, vengono eseguiti problemi di programmazione lineare sul modello presentato in questo articolo?
THE END

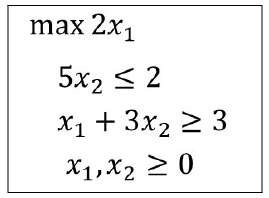
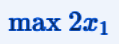

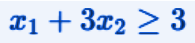
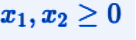
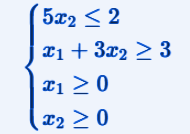

Great algebra teaching technique, sir.Although I have never been able to learn in such detail, I have passed the time.Thank you sir for clarifying the concepts again.
This is an Operations Research exercise and Operations Research is based on mathematics. What Operations Research wants to do is to transform real systems into mathematical systems and study them. In this way, predictions can be made or decisions can be taken with greater awareness.
This post has been upvoted by @italygame witness curation trail
If you like our work and want to support us, please consider to approve our witness
Come and visit Italy Community
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.