The Battle of the Blockchains - Tron vs. Ethereum duel
Tether (USDT), the world's most popular stablecoin, has become an integral part of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the US dollar, USDT offers stability in a volatile market and facilitates trading across various exchanges and platforms. But USDT isn't confined to a single blockchain. It exists on several, with Tron and Ethereum being the two dominant players.
Understanding the differences between USDT on Tron and Ethereum is crucial for traders, investors, and anyone operating within the digital asset space.
This article dives into the key distinctions between USDT on Tron (TRC-20) and Ethereum (ERC-20), exploring their pros and cons to help you make informed decisions.
The Basics: TRC-20 and ERC-20
Before I delve into the nuances, let's understand the underlying technologies:
ERC-20: This is the standard token contract for creating and issuing tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. It's the original and most widely recognized standard for tokens on Ethereum.
TRC-20: This is the technical standard for tokens issued on the Tron blockchain. While inspired by ERC-20, it offers different characteristics and functionalities tailored to the Tron network.
Key Differences: Transaction Fees, Speed, and Scalability
The primary differences between USDT on Tron and Ethereum boil down to transaction fees, speed, and scalability:
Transaction Fees:
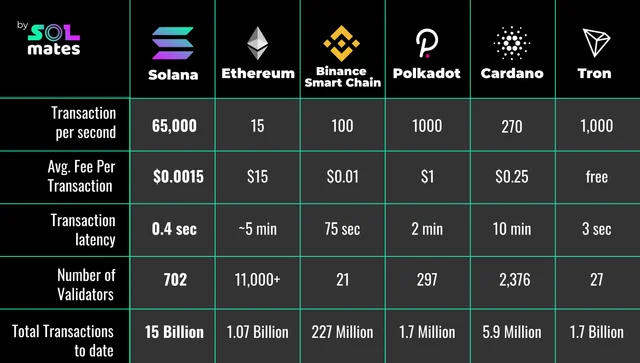
This is arguably the most significant differentiator. Tron boasts significantly lower transaction fees for USDT transfers compared to Ethereum. Ethereum's fees, often referred to as "gas fees," can fluctuate dramatically depending on network congestion, sometimes making small USDT transfers prohibitively expensive. Tron's fees, on the other hand, are typically a fraction of a cent, making it more appealing for frequent or smaller transactions.
Transaction Speed:
Tron generally offers faster transaction confirmation times than Ethereum. Tron boasts faster block times, leading to quicker settlement of USDT transfers. While Ethereum's transaction speeds have improved with ongoing upgrades, Tron usually maintains a noticeable edge.
Scalability: Tron is designed for higher transaction throughput compared to Ethereum's original architecture. This translates to a potentially smoother user experience during periods of high network activity, particularly concerning USDT transfers. While Ethereum is actively developing scaling solutions (like Layer 2 solutions), Tron currently handles a larger volume of transactions more efficiently.
Pros and Cons: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Let's summarize the advantages and disadvantages of each blockchain for USDT transactions:
USDT on Tron (TRC-20):
Pros:
Lower Transaction Fees: Significantly cheaper than Ethereum, especially for smaller transfers.
Faster Transaction Speed: Quicker confirmation times due to faster block times.
Higher Scalability: Can handle more transactions efficiently.
Cons:
Less Decentralized: Tron's blockchain is considered less decentralized compared to Ethereum.
Security Concerns: While Tron aims for security, it hasn't been as extensively battle-tested as Ethereum.
Ecosystem: While growing, Tron's ecosystem of DeFi and applications is still smaller than Ethereum's.
USDT on Ethereum (ERC-20):
Pros:
More Decentralized: Ethereum is widely considered one of the most decentralized blockchains.
Stronger Security: Ethereum's blockchain has a longer track record and has undergone extensive security audits.
Larger Ecosystem: Ethereum boasts a vast and vibrant ecosystem of DeFi protocols, decentralized applications (dApps), and other tools integrating ERC-20 tokens.
Cons:
Higher Transaction Fees: Gas fees can be prohibitively expensive, especially during peak network activity.
Slower Transaction Speed: Transaction confirmation times can be slower compared to Tron.
Scalability Issues: Historically faced scalability challenges, although improvements are being made.
Choosing the Right Blockchain: Factors to Consider
The best choice between USDT on Tron and Ethereum depends on your specific needs and priorities:
- Transaction Frequency and Size: If you make frequent and small USDT transfers, Tron is likely the more cost-effective option.
- Urgency: If transaction speed is critical, Tron generally offers faster confirmation times.
- Security Concerns: If security and decentralization are paramount, Ethereum might be preferred, despite the higher costs.
- DeFi Involvement: If you plan to utilize USDT within the DeFi ecosystem, Ethereum offers a much wider range of protocols and applications.
- Exchange Support: Most exchanges support both TRC-20 and ERC-20 versions of USDT, but it's always wise to confirm beforehand.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Landscape
The landscape of USDT is multifaceted, with Tron and Ethereum offering distinct advantages and disadvantages. While Tron offers lower fees and faster transactions, Ethereum prioritizes decentralization, security, and a larger ecosystem.
Understanding these differences is crucial for navigating the cryptocurrency world and making informed decisions about how to use and transfer USDT.
As both blockchains continue to evolve and innovate, it's essential to stay informed about the ongoing developments and their potential impact on USDT's functionality and utility. Ultimately, the "best" choice remains subjective and depends on your individual needs and preferences.